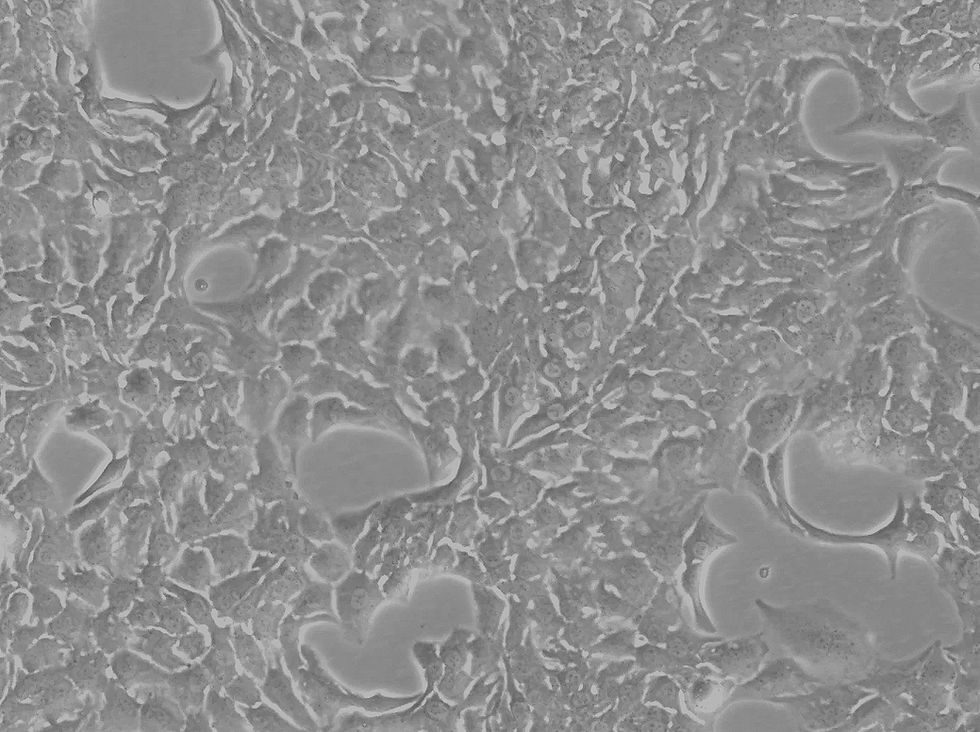
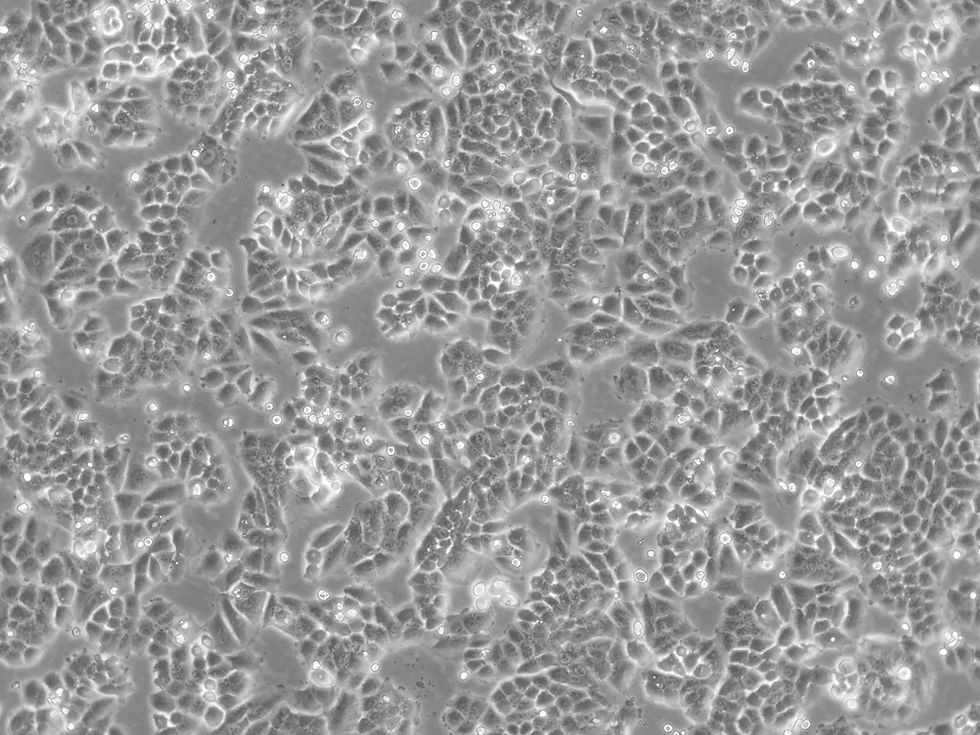
Parental Cell Lines
Reliable Foundations for Your Research
Our parental cell line collection provides researchers with high-quality, well-characterized cellular models designed to support reliable and reproducible research.
Each line is carefully expanded, authenticated, and quality controlled to ensure robust growth, stable morphology, and dependable experimental performance. Whether you are developing reporter assays, engineering stable cell models, or conducting functional genomics studies, our parental cells serve as a trusted foundation for your work, and all lines are verified to be mycoplasma-free for added confidence in your experiments.
Principle
A parental cell line is a group of cells that are derived from the same source or organism and are used as a starting point for creating different cell lines. Parental cell lines are often used in biomedical research and drug development to establish a baseline or control group for comparison purposes.
Parental cell lines can also be used to produce biologics, such as monoclonal antibodies or recombinant proteins, which are used as therapeutics. In this case, the parental cell line serves as the foundation for the production of these products.
Key Benefits
-
More than 30 well‑characterized, mycoplasma‑free parental cell lines.
-
Proven backbones for Signosis TF stable reporter and other engineered cell models.
-
Stable growth and good transfection/transduction efficiency for reliable experiments.
-
Flexible platforms for reporters, knockout, overexpression, and custom assays.
-
High quality at a competitive price—ideal for screening, scale‑up, and long‑term projects.
Products
Species | Product | SKU | Price (USD$) |
|---|---|---|---|
Human | HeLa | PC-001 | $422.00 |
Human | HEK293 | PC-002 | $422.00 |
Human | A549 | PC-003 | $422.00 |
Mouse | NIH/3T3 | PC-004 | $422.00 |
Human | HepG2 | PC-005 | $422.00 |
Human | Jurkat | PC-006 | $422.00 |
Human | K562 | PC-007 | $422.00 |
Human | MCF7 | PC-008 | $422.00 |
Human | HCC827 | PC-009 | $422.00 |
Monkey | COS-7 | PC-010 | $422.00 |
Insect | SF9 | PC-011 | $422.00 |
Chinese hamster | CHO-K1 | PC-012 | $422.00 |
Chinese hamster | CHO | PC-013 | $422.00 |
Human | AGS | PC-014 | $422.00 |
Human | HT-29 | PC-015 | $422.00 |
Human | MDA‑MB‑231 | PC-016 | $422.00 |
Mouse | MEF | PC-017 | $422.00 |
Mouse | B16-F10 | PC-018 | $422.00 |
Human | LNcaP | PC-019 | $422.00 |
Human | HCT 116 | PC-020 | $422.00 |
Human | HaCaT | PC-021 | $422.00 |
Mouse | C2C12 | PC-022 | $422.00 |
Human | LentiPack 293T | PC-023 | $445.00 |
Human | BxPC‑3 | PC-024 | $422.00 |
Dog | MDCK | PC-025 | $422.00 |
Human | MIA PaCa‑2 | PC-026 | $422.00 |
Human | NCI-H460 | PC-027 | $422.00 |
Mouse | Neuro2a | PC-028 | $422.00 |
Human | RKO | PC-029 | $422.00 |
Human | Ramos | PC-030 | $422.00 |
Human | U-937 | PC-031 | $422.00 |
Mouse | WEHI-3 | PC-032 | $422.00 |
Human | SK-OV-3 | PC-033 | $422.00 |
Human | U266 | PC-034 | $422.00 |
Human | AN3 CA | PC-035 | $538.00 |
Human | THP-1 | PC-036 | $422.00 |
Client Inquiries